这是耗子叔发起的一个活动,每周为一个周期,需要完成以下内容
- Algrothm: leetcode算法题目
- Review: 阅读并且点评一篇英文技术文章
- Tip/Techni: 学习一个技术技巧
- Share: 分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章
[Algrothm] target-sum
problem
https://leetcode.com/problems/target-sum/
494. Target Sum
Medium
1037
54
You are given a list of non-negative integers, a1, a2, ..., an, and a target, S. Now you have 2 symbols + and -. For each integer, you should choose one from + and - as its new symbol.
Find out how many ways to assign symbols to make sum of integers equal to target S.
Example 1:
Input: nums is [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], S is 3.
Output: 5
Explanation:
-1+1+1+1+1 = 3
+1-1+1+1+1 = 3
+1+1-1+1+1 = 3
+1+1+1-1+1 = 3
+1+1+1+1-1 = 3
There are 5 ways to assign symbols to make the sum of nums be target 3.
Note:
The length of the given array is positive and will not exceed 20.
The sum of elements in the given array will not exceed 1000.
Your output answer is guaranteed to be fitted in a 32-bit integer.
思路
- 这题一看就是动态规划
- 再复习一遍思路
- 递归
- 存储
- bottom-up
我的解法
先来个简单的递归
import itertools
class Solution(object):
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums, S):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type S: int
:rtype: int
"""
def find_target_sum(nums, S):
if len(nums) == 2:
count = 0
for a,b in itertools.product([-1,1],[-1,1]):
if a*nums[0] + b*nums[1] == S:
count +=1
return count
return find_target_sum(nums[:-1], S - nums[-1]) + find_target_sum(nums[:-1], S + nums[-1])
if len(nums)==1 and (nums[0]==S or nums[0]== -1 *S):
return 1
elif len(nums)==1:
return 0
return find_target_sum(nums, S)
不出所料,果然超时了
然后利用存储优化以下递归
import itertools
class Solution(object):
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums, S):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type S: int
:rtype: int
"""
dp_stack = {}
def find_target_sum(nums, S):
ret = dp_stack.get({}_{}.format(len(nums),S)):
if ret:
return ret
if len(nums) == 2:
count = 0
for a,b in itertools.product([-1,1],[-1,1]):
if a*nums[0] + b*nums[1] == S:
count +=1
dp_stack[{}_{}.format(len(nums),S)] = count
return count
ret = find_target_sum(nums[:-1], S - nums[-1]) + find_target_sum(nums[:-1], S + nums[-1])
dp_stack[{}_{}.format(len(nums),S)] = ret
return ret
if len(nums)==1 and (nums[0]==S or nums[0]== -1 *S):
return 1
elif len(nums)==1:
return 0
return find_target_sum(nums, S)
虽然已经进行了优化,然而还是超时,所以最后用动态规划来解
class Solution(object):
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums, S):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type S: int
:rtype: int
"""
dp_stack = [None] * len(nums)
if nums[0] == 0:
dp_stack[0] = {0: 2}
else:
dp_stack[0] = {-1 * nums[0]: 1, nums[0]: 1}
for i in range(1, len(nums)):
preview_ret = dp_stack[i - 1]
tmp_dict = {}
for s, count in preview_ret.items():
tmp_dict[s + nums[i]]= tmp_dict.get(s + nums[i],0) + count
tmp_dict[s - nums[i]]= tmp_dict.get(s - nums[i],0) + count
dp_stack[i] = tmp_dict
ret = dp_stack[-1].get(S, 0)
return ret
改为了动态规划之后就ac了
solution
看了别人的Solution更加简洁,
- 没有必要存储整个序列,只需要前一刻的状态和此时的状态就可以了
- 也有用counter的方法来计算的,效果还不错
[Review] RL by David Silver
还是强化学习有关内容 https://github.com/wwxFromTju/awesome-reinforcement-learning-zh
内容比较多,并且独立完整,所有详细的内容记录在了这里 RL Course by David Silver
[Tip] python pandas
我对于pandas一直属于一个知道这个东西存在,简单用用也会用的状态,但是最近发现这个模块远比我用到的内容丰富,所以系统的看一下。
资料
学习步骤
因为工作中能接触到,在理解了整体的基础上用就可以了
- 首先熟悉它们的官方文档,掌握各个部分的功能。
- 参考使用这几个库的书籍和教程,理解其中的关键概念
- 实践,练习,不断的实践和练习
笔记
pandas特点
- DataFram快速高效,并且集成了索引
- 可读写不同的模式,CSV, txt, Microsoft Excel, Sql, HDF5
- 智能的数据对其,处理missing data。
- 灵活的数据reshpe和pivot
- 基于label的智能slicing,fancy indexing和subsetting,可用于处理大规模数据集
- Columns可以变,可以删除或者替换
- group by引擎可以用于聚合和转化数据
- 高性能的merge和join
- 分层轴索引提供了对高纬度数据的方便
- 时间序列功能,日期范围生成和频率转会,移动窗口统计,移动窗口线性回归、数据转化和滞后。
- 核心功能用C或者是Cpython写的,高性能
pandas一览
pandas由下面的部分组成
- 有标签的数组类型的数据结构,主要是Series和Dataram,Series是1D的,并且其中的元素都是一种类型,Datarame是2D的,有不同类似的Column
- index对象,可以支持axis索引,和多层次的继承索引
- 用于数据聚合的和转换的groupby引擎
- 日期生成器
- 输入输出工具
- 内存高校的稀疏存储,用于存储大部分数据是缺失的数据
- 滑动窗口统计,(滑动平均、滑动方差等)
所有的pandas对象都是可变对象,但是大部分的size是不可变的。
快速教程
官方的文档的快速tour基本覆盖到了介绍的特性,这里我就不再写一遍了。内容还可以,可以对照着敲一遍。
基本覆盖了
- Series和Dataram
- 选择数据
- 遗失数据
- 操作
- merge
- group
- reshape
- 时间序列
- 分类
- plot
- 输入输出
可以按照这几点来检查对pandas初步的掌握。
[Share] PRCV1028短视第一名解决方案技术解读
数据集
短视频
测评方法
同时看时间和精度
视频解码
- I 帧
- P 帧
- B 帧
多线程同时解I帧,解码基于FFmpeg
主流模型
- LSTM
- 3D卷积
- 双流
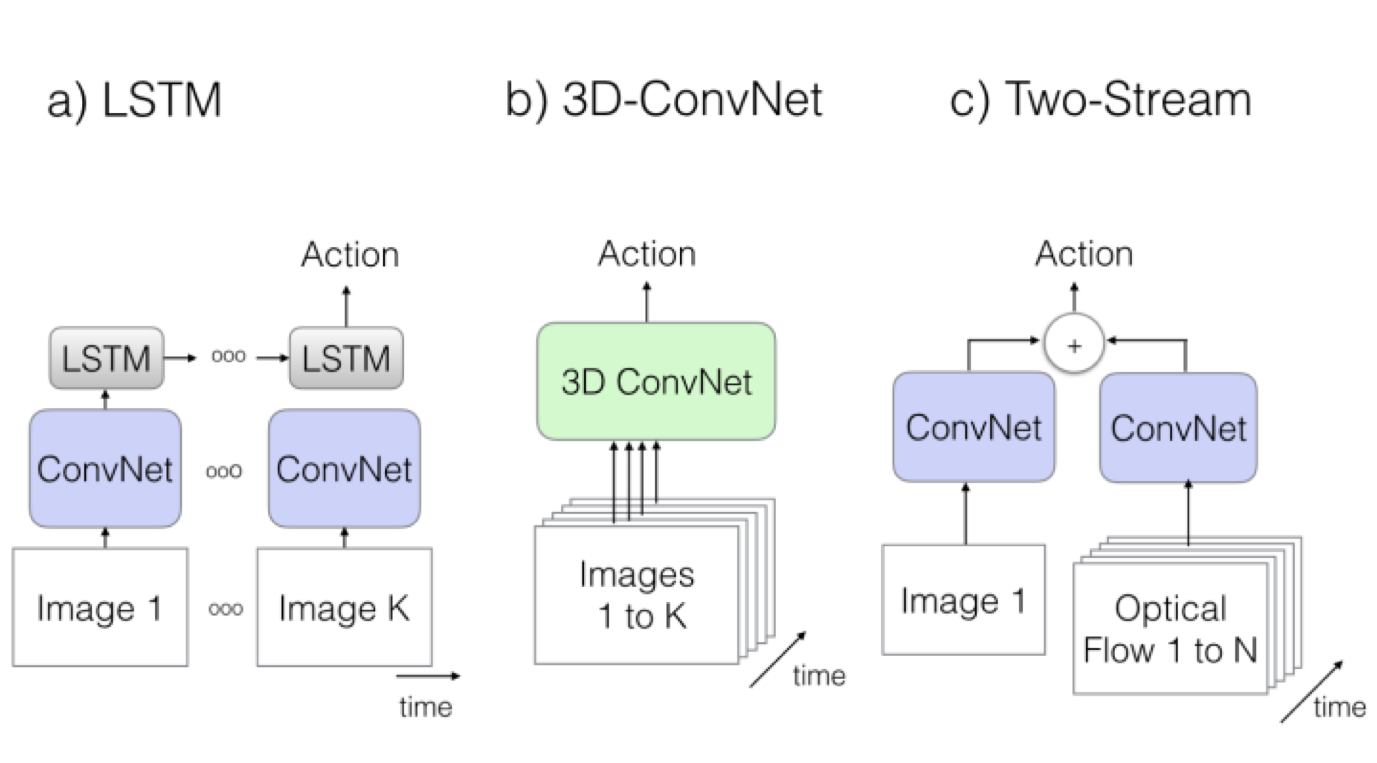
解决问题的模型
稀疏采样和帧间注意力模型
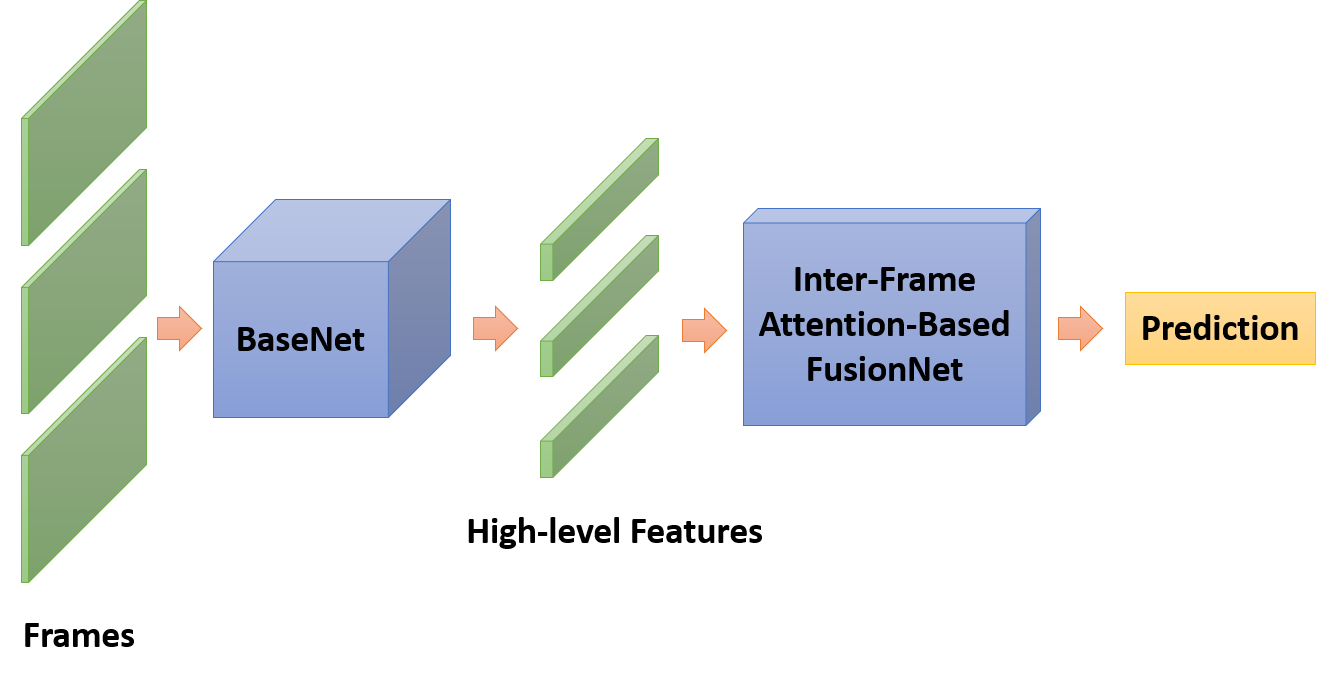
模型压缩
- 剪枝
- 量化