这是耗子叔发起的一个活动,每周为一个周期,需要完成以下内容
- Algrothm: leetcode算法题目
- Review: 阅读并且点评一篇英文技术文章
- Tip/Techni: 学习一个技术技巧
- Share: 分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章
[Algrothm]
之后刷题按照类型刷,这样有助于集中理解。正确一遍刷完之后能记住。 这里有一个 花花酱 整理的题目类型。
https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1SbpY-04Cz8EWw3A_LBUmDEXKUMO31DBjfeMoA0dlfIA/edit#gid=136677845
problem
870 Advantage Shuffle
870. Advantage Shuffle
Medium
Given two arrays A and B of equal size, the advantage of A with respect to B is the number of indices i for which A[i] > B[i].
Return any permutation of A that maximizes its advantage with respect to B.
Example 1:
Input: A = [2,7,11,15], B = [1,10,4,11]
Output: [2,11,7,15]
Example 2:
Input: A = [12,24,8,32], B = [13,25,32,11]
Output: [24,32,8,12]
Note:
1 <= A.length = B.length <= 10000
0 <= A[i] <= 10^9
0 <= B[i] <= 10^9
answer
有两个相同长度的数列,A 和 B ,通过交换 A 中元素的顺序,使得 A[i] > B[i] 的数量最多。
最简单的方法,
对A排序,对B排序,如果A<B ,pop A,
排序的时间复杂度是nlogn, pop的时间复杂度是 n , nlogn可以解。试试看。
solution
击败了 90% 的选手,
class Solution:
def advantageCount(self, A: List[int], B: List[int]) -> List[int]:
sorted_a = sorted(A,reverse=True)
sorted_b = sorted([(i, b) for i, b in enumerate(B)], key=lambda x: x[1],reverse=True)
length = len(B)
ret = [0] * length
a_index, b_index, a_tail_index = 0, 0, -1
while True:
if b_index >= length:
break
max_a = sorted_a[a_index]
now_b_i, max_b = sorted_b[b_index]
b_index = b_index + 1
if max_a > max_b:
ret[now_b_i] = max_a
a_index += 1
else:
ret[now_b_i] = sorted_a[a_tail_index]
a_tail_index -= 1
return ret
[Review]
[Tip]
vim 博大精深,继续学下vim,但是由于现在迁移到 pycharm 中了,有的 vim 功能不支持。
这里是一个 pycharm 下 vim 插件支持的功能列表:
https://github.com/JetBrains/ideavim/blob/master/src/com/maddyhome/idea/vim/package-info.java
阅读一下,看看有没有用用的
这个很有意思
* A. Misc commands
*
* tag handler
* -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
* |]b| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionCamelEndLeftAction}
* |]w| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionCamelEndRightAction}
* |[b| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionCamelLeftAction}
* |[w| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionCamelRightAction}
* |g(| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionSentencePreviousEndAction}
* |g)| {@link com.maddyhome.idea.vim.action.motion.text.MotionSentenceNextEndAction}
]b 按照驼峰规则移动到上个词的末尾
]w 按照驼峰规则移动到下个词的末尾
g( 移动到下个段落结束
g) 以后到上个段落结束
这个还有一个有意思的, vim 字母表
G 字母表
500 G 到第500行
[Share]
重新复习下容器技术
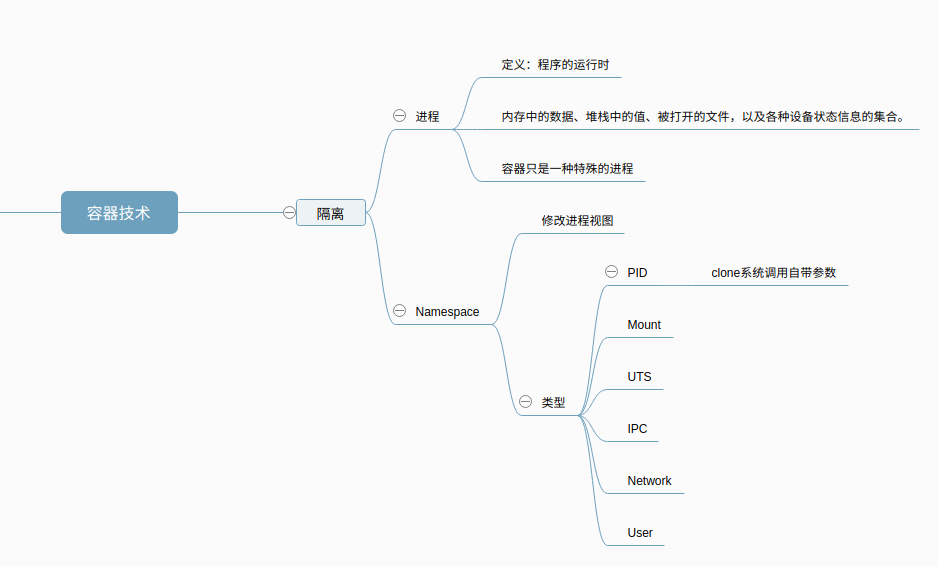
- 容器只是一类特殊的进程
- 容器视图是调用内核提供的NameSpace提供的隔离
- 常见的Namespace
- pid
- mount
- network
- user