这是耗子叔发起的一个活动,每周为一个周期,需要完成以下内容
ARTS:
- Algrothm: leetcode算法题目
- Review: 阅读并且点评一篇英文技术文章
- Tip/Techni: 学习一个技术技巧
- Share: 分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章
Algrothm
problem
https://leetcode.com/problems/arithmetic-slices/
A sequence of number is called arithmetic if it consists of at least three elements and if the difference between any two consecutive elements is the same.
For example, these are arithmetic sequence:
1, 3, 5, 7, 9
7, 7, 7, 7
3, -1, -5, -9
The following sequence is not arithmetic.
1, 1, 2, 5, 7
A zero-indexed array A consisting of N numbers is given. A slice of that array is any pair of integers (P, Q) such that 0 <= P < Q < N.
A slice (P, Q) of array A is called arithmetic if the sequence:
A[P], A[p + 1], ..., A[Q - 1], A[Q] is arithmetic. In particular, this means that P + 1 < Q.
The function should return the number of arithmetic slices in the array A.
Example:
A = [1, 2, 3, 4]
return: 3, for 3 arithmetic slices in A: [1, 2, 3], [2, 3, 4] and [1, 2, 3, 4] itself.
answer
- 先找到所有三个都是序列
- 然后向后扩充,向前扩充是没有必要的,不然就重复了
class Solution(object):
class Solution(object):
def numberOfArithmeticSlices(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
def is_sequence(a):
if 2 * a[1] == a[0] + a[2]:
return True
else:
return False
def find_all_after(A, sequence):
n = 0
a, index = sequence
tail = index + 2
tail_number = a[2]
intervel = a[2] - a[1]
while True:
tail += 1
if tail >= len(A) or A[tail] - tail_number > intervel:
break
elif A[tail] - tail_number == intervel:
tail_number = A[tail]
n += 1
return n
# in this problem it's not necessary to sort
# A.sort()
seqs = [(A[i:i + 3], i)
for i in range(len(A) - 3 + 1) if is_sequence(A[i:i + 3])]
n = len(seqs)
for seq in seqs:
n = n + find_all_after(A, seq)
return n
算法复杂度是 n^2
solution
看看更好的解法,这道题的正解是用动态规划来做
class Solution(object):
def numberOfArithmeticSlices(self, A):
"""
:type A: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
dp = [0]*len(A)
sum = 0
for i in range(2,len(A)):
if A[i] - A[i-1] == A[i-1] -A[i-2]:
dp[i] = 1 + dp[i-1]
sum +=dp[i]
return sum
dp理解
动态规划不是很熟,所以没有找到最好的方法
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=vYquumk4nWw
递归

如果采用递归的方式来计算fib,机会重复计算很多中间的状态,例如,fib(3),fib(2)。这样比较低效。
所以可以把中间的状态存储下来
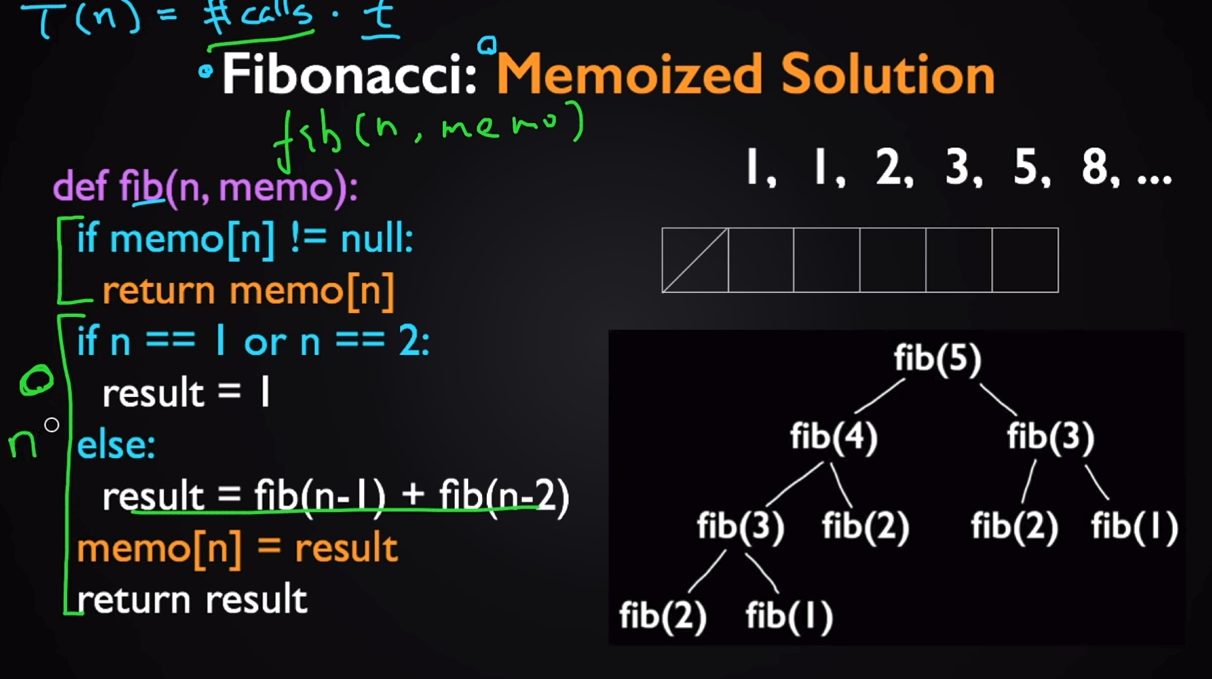
然后改为从0开始的方式
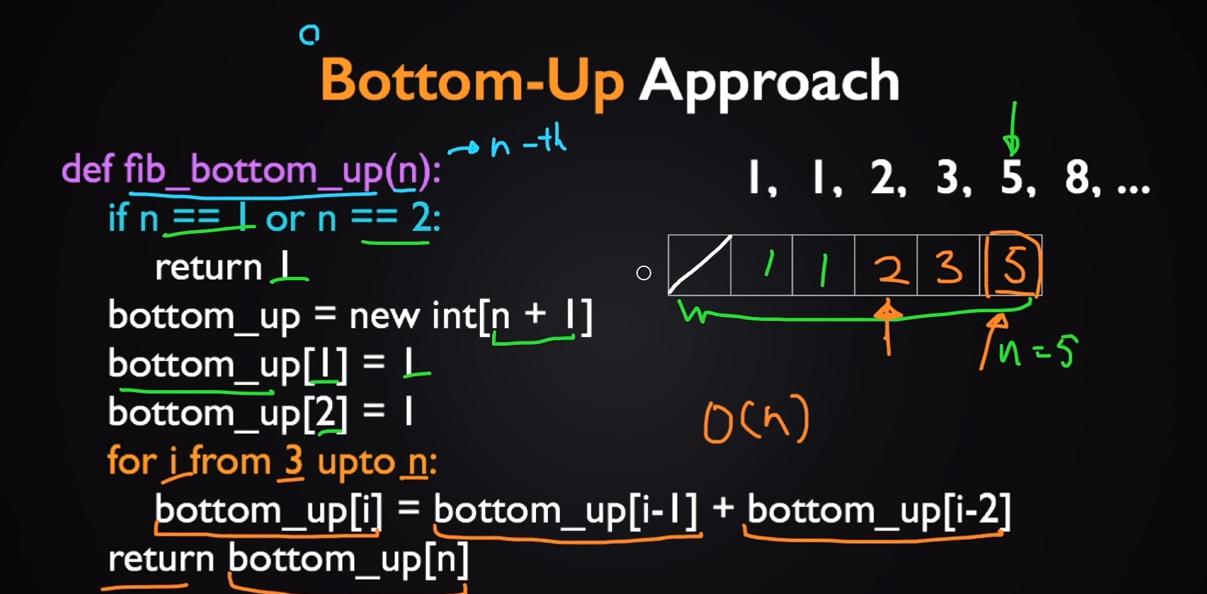
所以dp的思路基本是
- 递归
- 存储
- 改为从头开始
Review
文章
https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/02/using-machine-learning-to-predict.html
review
解决问题的方法
本文说明google map如何帮助用户找车位的。
问题难点
预测车位的问题有以下困难:
- 影响因素多,时间、工作日,天气,特殊事件,节假日。并且也没有realtime的车位数据。
- 有数据和网络链接的停车场,存在乱停车,等行为导致数据不准。
- 道路构成了一个大致的图,但是停车的结构更加复杂,因为交通流量可能会跨越不同的登记。
- 车位的供求都在不断变化,因此数据可能马上过时。
解决问题的方法:
通过ML和众包(crowdsourcing)的结合,提供给用户,停车的难度,让用户自己选择。
方法细节
获取数据
通过众包的方式,获取量化的数据:找到一个停车位要多久。数据量有100K。
模型特征
特征选择的不好,很容易使学习系统被误导,例如出租车,私人停车这些信息。
最后发现如果车一直绕来绕去,可能表示车位不够了:

选取了,直接到达和一直绕来绕去的用户的差异,还有其他特征,停车位的分散程度、时间、历史停车数据等等,最后大概有二十个不同的特征。
模型选择和训练
采用逻辑回归模型。
- 处理噪声的效果比较好
- 模型是白盒,易解释
- 输出易解释
结果

总结
ML的方法选择的比较简单,但是对数据和特征的选择花费了比较多的篇幅。采取众包的方法来获取数据。
Tip
vim
https://itsfoss.com/pro-vim-tips/
Original text
Pros:
* Fast
* Powerfull
* Reliable
* Not user-friendlyCons:
* Portable
* Addictive
Commands
/Power/ Go to the first line containing the string ‘Power’
ddp Swap the current line with the next one
:/user-friendly/m$ Move the next line containing the string ‘user-friendly’ to the end of the file
g; Bring back cursor to the previous position
:/Cons/+1m-2 Move two lines up the line following ‘Cons’
Modified text
Pros:
* Fast
* Reliable
* Powerfull
* PortableCons:
* Addictive
* Not user-friendly
执行当前python文件:
:! python %:p
!执行命令 python 调用python %:p 当前文件的完整路径
Share
本文讲述了强化学习相关的领域近况 https://www.jiqizhixin.com/articles/110402