这是耗子叔发起的一个活动,每周为一个周期,需要完成以下内容
ARTS:
- Algrothm: leetcode算法题目
- Review: 阅读并且点评一篇英文技术文章
- Tip/Techni: 学习一个技术技巧
- Share: 分享一篇有观点和思考的技术文章
Algrothm
problem
https://leetcode.com/problems/print-binary-tree/
Print a binary tree in an m*n 2D string array following these rules:
The row number m should be equal to the height of the given binary tree.
The column number n should always be an odd number.
The root node's value (in string format) should be put in the exactly middle of the first row it can be put. The column and the row where the root node belongs will separate the rest space into two parts (left-bottom part and right-bottom part). You should print the left subtree in the left-bottom part and print the right subtree in the right-bottom part. The left-bottom part and the right-bottom part should have the same size. Even if one subtree is none while the other is not, you don't need to print anything for the none subtree but still need to leave the space as large as that for the other subtree. However, if two subtrees are none, then you don't need to leave space for both of them.
Each unused space should contain an empty string "".
Print the subtrees following the same rules.
Example 1:
Input:
1
/
2
Output:
[["", "1", ""],
["2", "", ""]]
Example 2:
Input:
1
/ \
2 3
\
4
Output:
[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],
["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],
["", "", "4", "", "", "", ""]]
Example 3:
Input:
1
/ \
2 5
/
3
/
4
Output:
[["", "", "", "", "", "", "", "1", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["", "", "", "2", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "5", "", "", ""]
["", "3", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]
["4", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", ""]]
Note: The height of binary tree is in the range of [1, 10].
思路
- 广度优先获取每层元素
- 按照层次关系将每层扩展到
depth**2-1长度
对于一个三层的满树有
宽度搜索获取每层
[[1], 0
[2],[3],
[4],[5],[6],[7]]
需要变成的目标
[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],
["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],
["4", "", "5", "", "6", "", "7"]]
index变化
0 -> 3
0, 1 -> 1, 5
0, 1, 2, 3 -> 0, 2, 4, 6
规律
假设总depth = n, 当前depth 为 i, res = n-i
首元素 index = 2**(res) -1
其他元素 = 首元素index + 2**(res+1) * index
通项: new_index = 2**(res) - 1 + 2**(res+1) * index
可以可以利用numpy的特性简化计算
import numpy as np
class Solution(object):
def printTree(self, root):
"""imporpt
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
def extend_layer(final_depth, current_depth, layer):
res_depth = final_depth - current_depth
final_length = 2 ** final_depth - 1
index = np.array(range(len(layer)))
new_index = 2 ** res_depth - 1 + 2 ** (res_depth + 1) * index
extended_layer = [""] * final_length
for i in range(len(layer)):
extended_layer[new_index[i]] = layer[i]
return extended_layer
result = [[str(root.val)]]
now_layer = [root]
depth = 1
while True:
next_layer = []
for node in now_layer:
if not node:
next_layer.append(None)
next_layer.append(None)
continue
next_layer.append(node.left)
next_layer.append(node.right)
next_layer_val = [str(node.val) if node else "" for node in next_layer]
if all([val is '' for val in next_layer_val]):
break
result.append(next_layer_val)
now_layer = next_layer
depth += 1
print(result)
extended_ret = []
for i, line in enumerate(result):
current_depth = i + 1
extended_ret.append(extend_layer(depth, current_depth, line))
return extended_ret
solution
在leetcode上也附带了解析的答案有两个
第一个是利用递归的方法来进行
public class Solution {
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
int height = getHeight(root);
String[][] res = new String[height][(1 << height) - 1];
for(String[] arr:res)
Arrays.fill(arr,"");
List<List<String>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
fill(res, root, 0, 0, res[0].length);
for(String[] arr:res)
ans.add(Arrays.asList(arr));
return ans;
}
public void fill(String[][] res, TreeNode root, int i, int l, int r) {
if (root == null)
return;
res[i][(l + r) / 2] = "" + root.val;
fill(res, root.left, i + 1, l, (l + r) / 2);
fill(res, root.right, i + 1, (l + r + 1) / 2, r);
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left), getHeight(root.right));
}
}
第二个是利用宽度优先搜索
与这次的答案类似,只是将扩展和宽度优先的搜索放在一起做了。
利用递归的思路写的内容相对代码量比较小,负责度为 O(2**h),h是树的高度
Review
因为最近再看强化学习方面的内容,所以找了一tour性质的文章看一下
文章:
强化学习教程:从持续控制的角度出发
A Tour of Reinforcement Learning: The View from Continuous Control
内容
Abstract
这篇文章是一片讲述强化学习的文章,文章中讲述了常用的公式,术语和常用的实现。 为了便于说明,这篇文章中会利用LQR(Linear Quadratic Regulator)的这个优化中的例子。
Introduction
强化学习是机器学习下的一个域。事实上在控制理论中也存在类似的问题。这篇文件主要介绍了在强化学习中的一些概念等。
控制是从一个定义好的模型中设计一套复杂的行为;强化学习可以从数据中进行复杂的,无模型的预测。然而这两个领域要解决的问题是相同的。文中会说明他们区别。
首先文章会将RL问题转化为优化问题。然后分别讲述model-free 和 model-based 的方法论。然后会通过LQR的例子将RL和控制技术结合起来。
什么是强化学习
控制理论的问题背景
控制理论解决是下面这个问题:
maximize $E_{et}[\sum_{t=0}^NR_t[x_t,u_t]+ R_{N+1}(x_{N=1})]$
subject to $x_{t+1} = f_t(x_t,u_t,e_t)$
$x_t$是t时间系统的状态,$u_t$表示控制操作,$e_t$是一些随机干扰,$f_t$是从前面三个状态得到下个系统状态的映射,$R_t[x_t,u_t]$表示$x_t,u_t$带来的回报。
正对整个动态的情况做优化过于复杂,因此,引入$\pi$,它表示根据历史信息产生新action的映射
maximize $E_{et}[\sum_{t=0}^NR_t[x_t,u_t]+ R_{N+1}(x_{N=1})]$
subject to $x_{t+1} = f_t(x_t,u_t,e_t),u_t = \pi_t(T_t)$ $T_t =(u1,…,ut-1,x_0,…,x_t)$
但是如果我们对状态转移方程$f_t$一无所知,或者,$f_t$非常复杂,需要耗费大量的资源,我们如何解决这类问题。
强化学习的trade-off: 有效,然而难以解释。并且失败可能导致灾难性的后果。
解决强化学习问题的策略
基于模型的强化学习
maximize $E_{et}[\sum_{t=0}^NR_t[x_t,u_t]+ R_{N+1}(x_{N=1})]$
subject to $x_{t+1} = \hat\varphi(x_t,u_t) + w_t,u_t = \pi_t(T_t)$
这里的$w_t$表示用于模型噪音处理的一个模型,我们通过机器学习的方法得到$\hat \varphi$,如果它能够近似与$f_t$那么效果是不错的。
Approximate Dynamic Programming 类动态规划
这种方法直接针对 control cost做优化,并且利用了动态规划的一些技术。
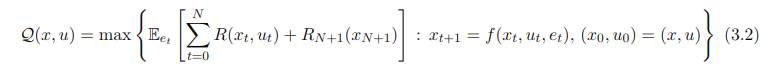
直接搜索策略
抽样优化
最优化 $ maximize_{z}R(z)$事实上等同于优化z的概论分布: $maxmize_{p(z)} E_p[R(z)]$
如果直接优化$p(z)$是比较苦难的,所以我们可以考虑由参数向量参数化的族$\thetasym:p(u;\thetasym)$
$maximize_\thetasym E_p(z;\thetasym)[R(z)]$
如果这个族的分布有 Delta functions,就会变成一个非随机变量的优化问题。
考虑Delta function有下面的式子
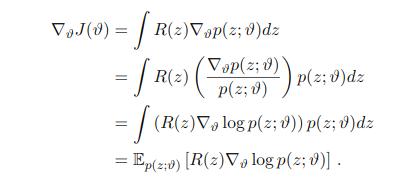
其中$J(\thetasym):=E_p(z;\thetasym)[R(z)]$
这样就能使用梯度下降的方法来求解这个问题
 有两种搜索方式
有两种搜索方式
Policy Gradient
就是利用梯度下降的方法来进行搜索,对$\thetasym$来进行有方向的更新。
纯随即搜索
深度强化学习
深度学习不是单独的强化学习的方式,在上面所有方式中都可以利用神经网络。
- 基于模型的学习,$\varphi$,可以是一个神经网络
- 在ADP中,Q-functions 和 Value Function可以通过神经网络来拟合
- 在策略搜索中,策略可以被设置为神经网络。
总结
目前对很多背景只是太过模糊,直接阅读这篇文章感觉感觉很差。所以重新读了几遍,放弃了要完全看懂的想法。只是理解了一个脉络
下周看看下相关的背景资料: https://github.com/wwxFromTju/awesome-reinforcement-learning-zh
Tip
用cProfile来分析代码性能 例子
def test():
print('hello')
with open('test','w') as f:
f.write('hello')
import cProfile
cProfile.run('test()')
结果,可以看到函数的调用情况。这个有时候用于做性能分析很有用。
$ python haha.py
hello
5 function calls in 0.000 seconds
Ordered by: standard name
ncalls tottime percall cumtime percall filename:lineno(function)
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 <string>:1(<module>)
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 haha.py:1(test)
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'disable' of '_lsprof.Profiler' objects}
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {method 'write' of 'file' objects}
1 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 {open}
Share
为什么三五个人一个大隔间效率高。